Fundamentals of digital systems
CS-173
Media
05-Mar-24 Tutorial on Logisim Evolution (Basics)
05.03.2024, 10:55
Author: Emma Gaia Poggiolini
CS-173 Fundamentals of Digital Systems
05-Mar-24
EPFL
This is a basic introduction to Logisim Evolution.
18-Mar-24
18.03.2024, 15:40
Welcome
 Lectures
Lectures
The course can be followed in person in CO1 or as a live stream. Two rooms are reserved for those preferring the live stream while on campus:
- INM 202 on Mondays, from 13:15 to 15:00 and
- INM 200 on Thursdays, from 14:15 to 15:00.
Exercises
Rooms: INF1, INF2, INF3Schedule: Mondays from 15:15 to 17:00 and Thursdays from 15:15 to 17:00
Exercises are organized as Q&A sessions, during which you will be expected to try solving several problems related to the ongoing lectures. The exercise material will be posted on Moodle: one pdf file will contain the problems to solve and one the solutions. The latter will be made public at the end of the exercise session.
- Announcements (Forum)
- Course videos on EPFL Mediaspace (URL)
- Coursebook (URL)
- Course on the web (URL)
- Course schedule (File)
- Virtual Machine (URL)
- Instructions for using the software tools (File)
- Exercise Book (File)
- Verilog - Coding Guidelines (File)
- Verilog - Example of style guidelines (URL)
- Verilog - Troubleshooting and Tips (File)
- The RISC-V Instruction Set Manual (URL)
- RV32I Reference Card (File)
 Lectures
LecturesMonday
Agenda
- Introduction to the course
- Number systems
- unsigned integers
- signed integers
- sign-and-magnitude
- two's complement
- binary, octal, hexadecimal numbers
- sign extensions and arithmetic shifts
- Flipped classroom:
- Hamming weight and distance
- Gray and BCD codes
Literature
- Wakerly, Chapter 2: Number Systems and Codes
- 2.1-2.3
- 2.5
- 2.10-2.11
- Ercegovac and Lang, Chapter 1: Preview of Basic Number Representations and Arithmetic Algorithms
- 1.1,-1.2
- 1.4
- Brown and Vranesic, Chapter 3: Number Representation and Arithmetic Circuits
- 3.1
- 3.3.1
Agenda
- Binary addition/subtraction/multiplication
- unsigned
- signed
- Overflow
Literature
- Wakerly, Chapter 2: Number Systems and Codes
- 2.6
- 2.8
- Ercegovac and Lang, Chapter 1: Preview of Basic Number Representations and Arithmetic Algorithms
- 1.3
- 1.5
- Brown and Vranesic, Chapter 3: Number Representation and Arithmetic Circuits
- 3.2, excluding digital circuit design
- 3.3.2, 3.3.5
- 3.6, excluding digital circuit design
- Announcement (Page)
- [Monday] Lecture - Welcome (File)
- [Monday] Lecture - Number systems, Part I (File)
- [Thursday] Lecture - Number systems, Part II (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Number systems (without solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Number systems (with solutions) (File)
Lectures

Monday
Agenda
- Number systems - Fractional (noninteger) numbers
- Fixed-point number representation
- Concepts of finite-precision math
- Precision
- Resolution
- Range
- Accuracy
- Dynamic range
- Floating-point number representation
- Significand, exponent, and base
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Special values
- Overflow and underflow
- IEEE Standard 754
Literature: Fixed-point number representation
- Ercegovac and Lang, Chapter 1: Preview of Basic Number Representations and Arithmetic Algorithms
- 1.2.5
- Brown and Vranesic, Chapter 3: Number Representation and Arithmetic Circuits
- 3.7.1
- On the web
Literature: Floating-point number representation
- Ercegovac and Lang, Chapter 8: Floating-Point Representation, Algorithms, and Implementations
- 8.1-8.3
- 8.4.1, 8.5.1
- Brown and Vranesic, Chapter 3: Number Representation and Arithmetic Circuits
- 3.7.2
- On the web
- Wiki, IEEE Standard for Floating-Point Arithmetic (IEEE 754), link
Agenda
- No new lecture
- Lecture - Number systems, Part III, Fractional numbers (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - Number systems (without solutions) (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - Number systems (with solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Number systems (without solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Number systems (with solutions) (File)
Monday
Agenda
- Number systems - Algorithms for arithmetic operations
- fixed-point
- floating-point
- Digital Logic and Design with Verilog - Introduction to Logic Circuits
- Variables and functions
- Truth tables
- Logic gates and networks
- Timing diagram
- Functionally equivalent networks
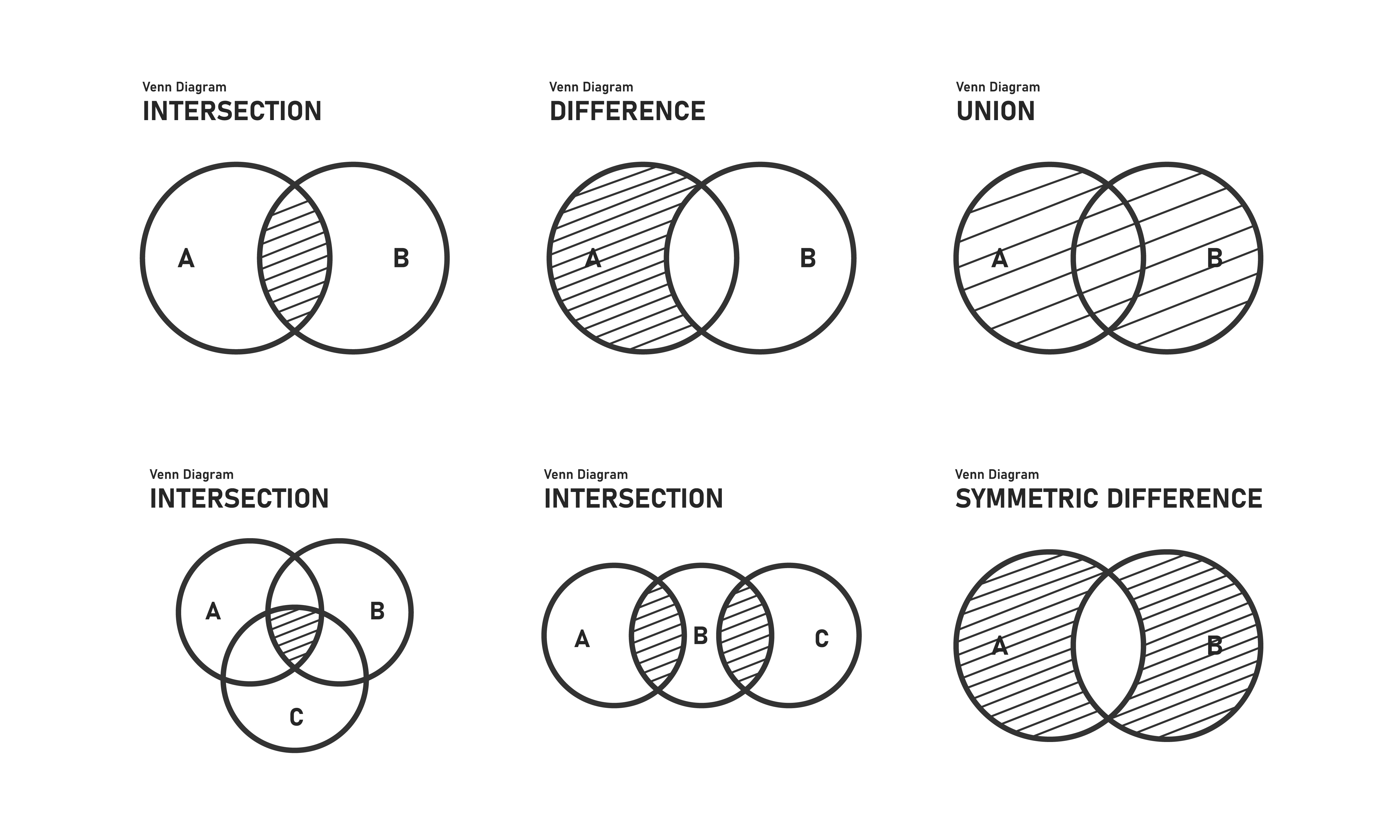
- Boolean algebra
- Axioms and theorems
- Venn diagram
- Precedence of operations
Literature: Introduction to Logic Circuits
- Wakerly, Chapter 1: Introduction
- 1.4, 1.5
- Wakerly, Chapter 3: Switching Algebra and Combinational Logic
- 3.1-3.3
- Wakerly, Chapter 4: Digital Design Practices
- 4.1.1-4.1.6
- Brown and Vranesic, Chapter 2: Introduction to Logic Circuits
- 2.1-2.5
Agenda
- Continuation of Monday's lecture
- Lecture - Number systems, Part IV, Fractional numbers arithmetic (File)
- Lecture - Digital logic, Part I, Logic gates and Boolean algebra (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - Number systems (without solutions) (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - Number systems (with solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Number systems (without solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Number systems (with solutions) (File)
Monday
Agenda
- Digital Logic and Design with Verilog - Introduction to Logic Circuits
- Synthesis using AND, OR, and NOT gates
- Sum-of-Products and Product-of-Sums forms
- NAND and NOR logic networks
- Don't cares
- XOR and XNOR gates
- Design examples
- Number display
- Multiplexer
Literature: Introduction to Logic Circuits
- Wakerly, Chapter 3: Switching Algebra and Combinational Logic
- 3.1-3.3
- Brown and Vranesic, Chapter 2: Introduction to Logic Circuits
- 2.6-2.8
Agenda
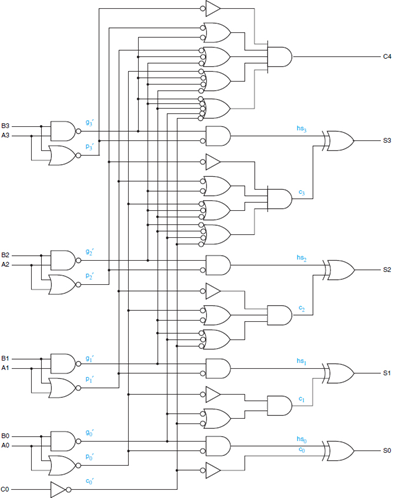
- Digital Logic and Design with Verilog - Combinational Arithmetic Circuits
- Adding and subtracting
- Shifting (barrel shifter)
Literature
- Wakerly, Chapter 8: Combinational Arithmetic Elements
- 8.1, 8.2
- Brown and Vranesic, Chapter 3: Number Representation and Arithmetic Circuits
- 3.2-3.4
- Lecture - Digital logic, Part II, Logic synthesis (File)
- Lecture - Digital logic, Part III, Arithmetic circuits (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - Digital logic (without solutions) (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - Digital logic (with solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Digital logic (without solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Digital logic (with solutions) (File)
Monday (Mirjana absent)
Agenda
- Finish the Combinational Arithmetic Circuits lecture
- Spring 2024 lecture video: Watch on MediaSpace
- Introduction to Logisim
- Watch our tutorial on Logisim Evolution: Watch on MediaSpace
- Explore videos in the literature section below
Literature
- Logisim Evolution, Visit GitHub
- Logisim Documentation, Visit GitHub
- Series of video tutorials on Logisim Evolution, Watch on YouTube
Thursday
Agenda
- Introduction to computer-aided design of integrated circuits and Verilog
Literature
- Brown and Vranesic, Chapter 4: Combinational Circuit Building Blocks
- 4.1-4.6
- Brown and Vranesic, Appendix A: Verilog Reference
- A.1-A.10
- Wakerly, Chapter 1: Introduction
- 1.9
- Wakerly, Chapter 7: More Combinational Building Blocks
- 7.1-7.4
- Wakerly, Chapter 5: Verilog Hardware Description Language
- 5.2-5.5
Selected literature on the history of Verilog for enthusiasts:
- Phil Moorby and the History of Verilog: Read the blog
- Verilog HDL and Its Ancestors and Descendants: Read the blog
- Announcement (Page)
- Lecture - Digital logic and Verilog, Part IV, Introduction to Verilog (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - Digital Logic (without solutions) (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - Digital logic (with solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Digital Logic (without solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Number Systems (without solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Digital Logic (with solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Number Systems (with solutions) (File)
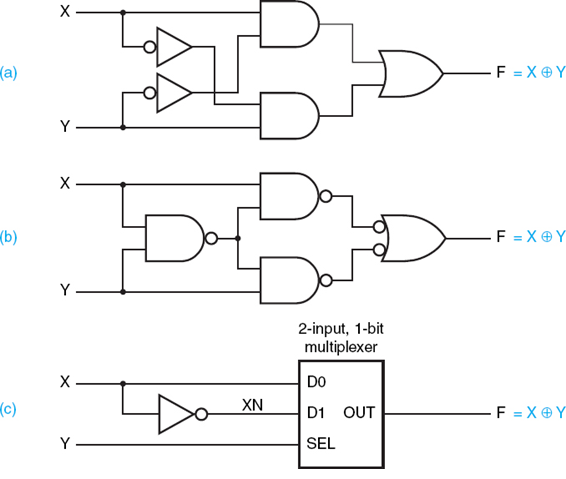
Monday
Agenda
- Digital Logic and Design with Verilog - Combinational Circuit Building Blocks
- Bus
- Multiplexers
- Tri-state buffers
- Verilog for combinational circuits
- Hands-on introduction to Icarus Verilog and GTKWave
- See Literature section below
- Introduction to Verilog HDL using Icarus, GTKWave, and VScode, Watch on YouTube
Literature
- Wakerly, Chapter 7: More Combinational Building Blocks
- 7.1-7.4
- Brown and Vranesic, Chapter 4: Combinational Circuit Building Blocks
- 4.1-4.6
- About Icarus Verilog, Visit Wikipedia
- Icarus Verilog on GitHub, Visit GitHub
- GTKWave documentation, Visit Sourceforge
- GTKWave, Visit GitHub
- Introduction to Verilog HDL using Icarus, GTKWave, and VScode, Watch on YouTube
Thursday
Agenda
- Implementation Technology
- Transistor switches
- NMOS and PMOS transistors
- CMOS logic gates
- Practical aspects
- Dynamic operation
- Fan-in and Fan-out in logic gates
- Power dissipation
- Real timing waveforms
- Timing hazards
- Transistor switches
Remind yourself of below circuit components and their voltage/current characteristics to be able to follow the lecture:
Literature
- Brown and Vranesic, Appendix B: Implementation Technology
-
- B.1-B.4
- B.8
- Wakerly, Chapter 14: Digital Circuits
- 14.1-14.5
- Lecture - Digital logic and Verilog, Part V, Verilog for combinational circuits (File)
- Lecture - Digital logic, Part VI, Implementation technology (File)
- [Monday] Exercises (Page)
- [Monday] Exercises - Digital Logic (without solutions) (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - Digital Logic (with solutions) (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - Logisim solution (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Digital Design with Verilog (without solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Digital Design with Verilog (with solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Digital Design with Verilog - Additional resources (Folder)
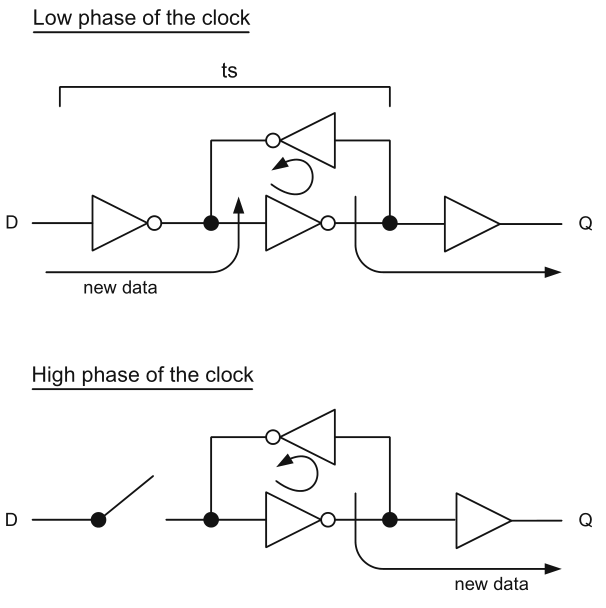
Monday
Agenda
- Digital Logic and Design with Verilog - Flip-flops, Registers, and Counters
- Latch
- Edge-triggered D flip-flop
- Verilog modeling of latches and D flip-flops
Literature
- Wakerly, Chapter 10: Sequential Logic Elements
- 10.2-10.4
- Brown and Vranesic, Chapter 5: Flip-Flops, Registers, and Counters
- 5.3, 5.4, 5.8-5.10, 5.13
Thursday
Agenda
- Digital Logic and Design with Verilog - Registers and Counters
- Registers
- Counters
- Verilog constructs for registers and counters
Literature
- Wakerly, Chapter 11: Counters and Shift Registers
- 11.1, 11.2
- Brown and Vranesic, Chapter 5: Flip-Flops, Registers, and Counters
- 5.3, 5.4, 5.8-5.10, 5.13
Exercises
- Digital Circuit Verification: Writing Testbenches in Verilog
- Tutorial
- [Not mandatory but potentially useful] Additional resources on the web
- Using Verilog for Testbenches [ETHZ], View pdf
- Very simple tutorial on YouTube Watch on YouTube
- Testbench example that can be executed on EDA playground, Visit Page
- Another deck of slides View pdf
- Chipverify, Visit Page
- Lecture - Digital logic and Verilog, Part VII, Sequential logic (File)
- Lecture - Digital logic and Verilog, Part VIII, Registers and counters (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - Digital Logic (without solutions) (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - Digital Logic (with solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Digital Design with Verilog (without solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Digital Design with Verilog (with solutions) (File)
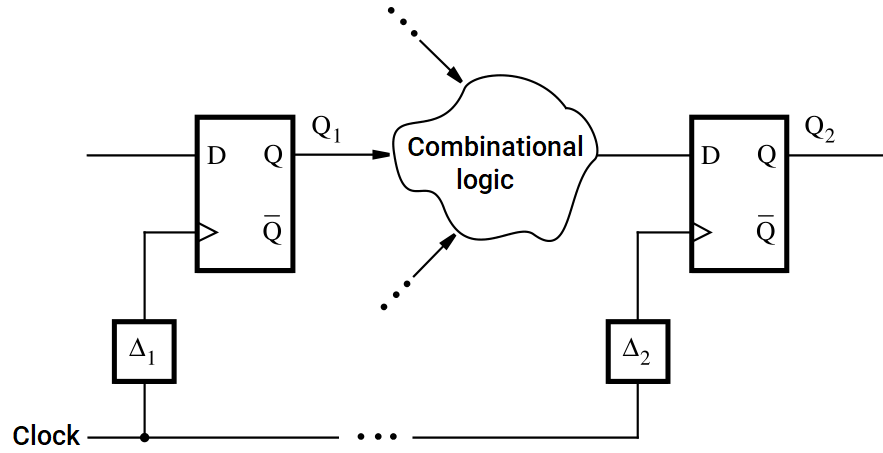
Agenda
- Digital Logic and Design with Verilog - Timing Analysis of Synchronous Circuits
- Flip-flop timing constraints and parameters
- Clock skew
- Metastability
- Synchronization of external asynchronous inputs
Literature
- Wakerly, Chapter 13: Sequential-Circuit Design Practices
- 13.3
- Brown and Vranesic, Chapter 5: Flip-flops, Registers, and Counters
- 5.15
Agenda
- Memory technology
- Two-dimensional array of FFs
- 2-to-2^n binary decoder
- Verilog
- Parameterized modules
- Conditional operator
Literature
- Brown and Vranesic, Chapter 4: Combinational-Circuit Building Blocks
- 4.2
- Brown and Vranesic, Appendix A: Verilog Reference
- A.6.3
- Lecture - Digital logic and Verilog, Part IX, Timing Analysis of Sequential Circuits (File)
- Announcement (Page)
- Lecture - Digital logic and Verilog, Part X, Memories (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Digital Design with Verilog (without solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Digital Design with Verilog (with solutions) (File)
- [Monday] Mock Midterm (without solutions) (File)
- [Monday] Mock Midterm (with solutions) (File)
Monday
Agenda
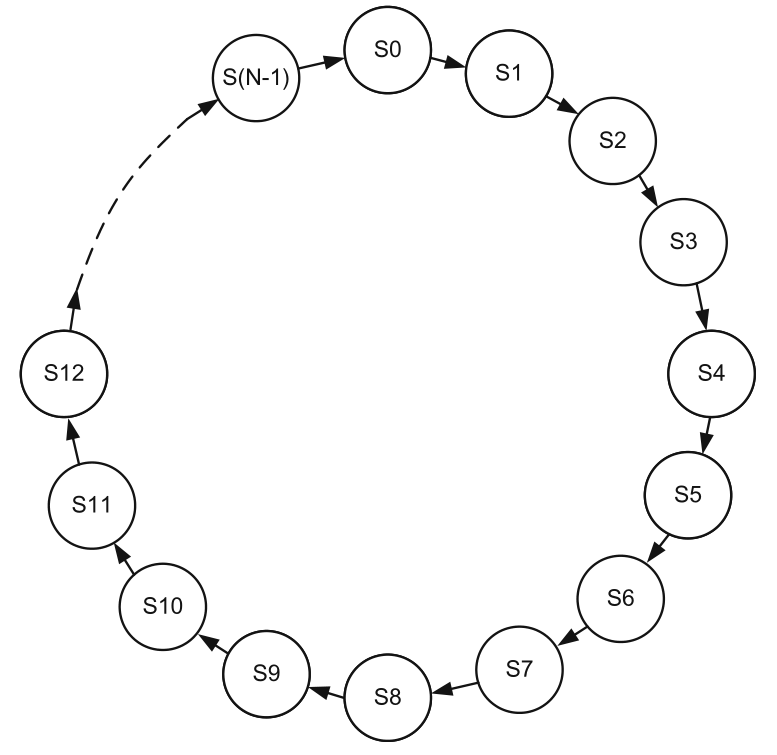
- Digital Logic and Design with Verilog - State Machines
- Basic design steps
- Mealy and Moore state machines
- State-machine design in Verilog
Literature
- Wakerly, Chapter 12: State Machines in Verilog
- 12.1, 12.2
- Brown and Vranesic, Chapter 6: Synchronous Sequential Circuits
- 6.1, 6.3, 6.4, 6.7
Agenda
- Finite State Machines - Examples
- Midterm Exam - April 14, 2025 @ 15:15 (Page)
- Lecture - Digital logic and Verilog, Part XI, Finite State Machines (File)
- Lecture - Digital logic and Verilog, Part XII, Examples of FSMs (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Sequential Circuits (without solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Sequential Circuits (with solutions) (File)
- Testbench for the counter circuit (tb_counter_circuit.v) (File)
 Semester break
Semester break Monday
Monday
Agenda
- Digital Logic and Design with Verilog
- Buses with tri-state drivers and multiplexers
- Reduction operators
- Generate statements and for loops
- Design examples:
- Register swapping
- Ripple-carry adder with a generate statement
Literature
- Brown and Vranesic, Chapter 6: Synchronous Sequential Circuits
- 6.5, 6.18
- Brown and Vranesic, Appendix A: Verilog Reference
- A.12.1, A.12.2, A.14.7
Thursday
Agenda
- Introduction to computer architecture
Literature
- Patterson and Hennessy, Chapter 4: The Processor
- 4.1 - 4.5
- Lecture - Digital logic and Verilog, Part XIII, Buses, reduction operators, generate statements (File)
- Lecture - Computer architecture, Part I, Intro to processors (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - FSMs (without solutions) (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - FSMs (with solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Timing analysis and FSMs (without solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - Timing analysis and FSMs (with solutions) (File)
 Monday
Monday
Agenda
- RISC-V Instruction Set Architecture
-
- Registers
- Computational instructions
- R-type: Register-register operations
- I-type and U-type: Register-immediate operations
- No operation: NOP pseudoinstruction
Literature
- RISC-V Instruction Set Manual (20240411): Read online
- 4.1 - 4.5
Thursday
Agenda
- No new lecture
- Announcement (Page)
- Update in Spring 2025 (Page)
- Lecture - Computer architecture, Part II, Registers and integer computations (File)
- The RISC-V Instruction Set Manual (20240411) (URL)
- [Monday] Exercises - Memory (without solutions) (File)
- [Monday] Testbench - Memory (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - Memory (with solutions) (File)
- [Thrusday] Exercises - Introduction to RISC-V (without solutions) (File)
- [Thrusday] Exercises - Introduction to RISC-V (with solutions) (File)
 Monday
Monday
Agenda
- RV32I ISA
- Memory
- General properties
- Byte order (endianness)
- Read (load) and write (store) instructions
- Control transfer instructions
- Conditional branches
- Unconditional jumps
- S/B/J instruction formats
- Memory
- mv pseudo instruction
- j pseudo instruction
- Examples in assembly
Literature
- RISC-V Instruction Set Manual (20240411): Read online
Thursday
Agenda
- Assembler directives
- Pseudoinstructions: load immediate (li) and load address (la)
- Do-while loop in assembly
- If-then-else in assembly
- Examples in assembly
- Lecture - Computer architecture, Part III, Memory access and branch instructions (File)
- Lecture - Computer architecture, Part IV, Assembler directives (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - RISC-V Assembly Programming (without solutions) (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - RISC-V Assembly Programming (with solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - RISC-V Assembly Programming (without solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - RISC-V Assembly Programming (with solutions) (File)
 Monday
Agenda
Monday
Agenda
- CPU Performance
- Single-cycle implementation of a simple RISC-V processor
Literature
- Patterson and Hennessy, Chapter 4: The Processor
- 4.5
Agenda
- Multi-cycle implementation of a simple RISC-V processor
- Lecture - Computer architecture, Part V, Performance and a single-cycle CPU (File)
- Single-cycle CPU schematic (File)
- Lecture - Computer architecture, Part VI, Multicycle CPU implementation (File)
- Multicycle CPU schematic (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - RISC-V Assembly Programming (without solutions) (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - RISC-V Assembly Programming (with solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - RISC-V Assembly Programming (without solutions) (File)
- [Thursday] Exercises - RISC-V Assembly Programming (with solutions) (File)
 Monday
Monday
Agenda
- Multi-cycle implementation of a simple RISC-V processor, contd.
- Exercise session: Mock Exam
Thursday
Bank Holiday
That's All Folks!
- Lecture - Computer architecture, Part VI, Multicycle CPU FSM (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - Mock Exam (without solutions) (File)
- [Monday] Exercises - Mock Exam (with solutions) (File)