Sensing and spatial modeling for earth observation
ENV-408
Media
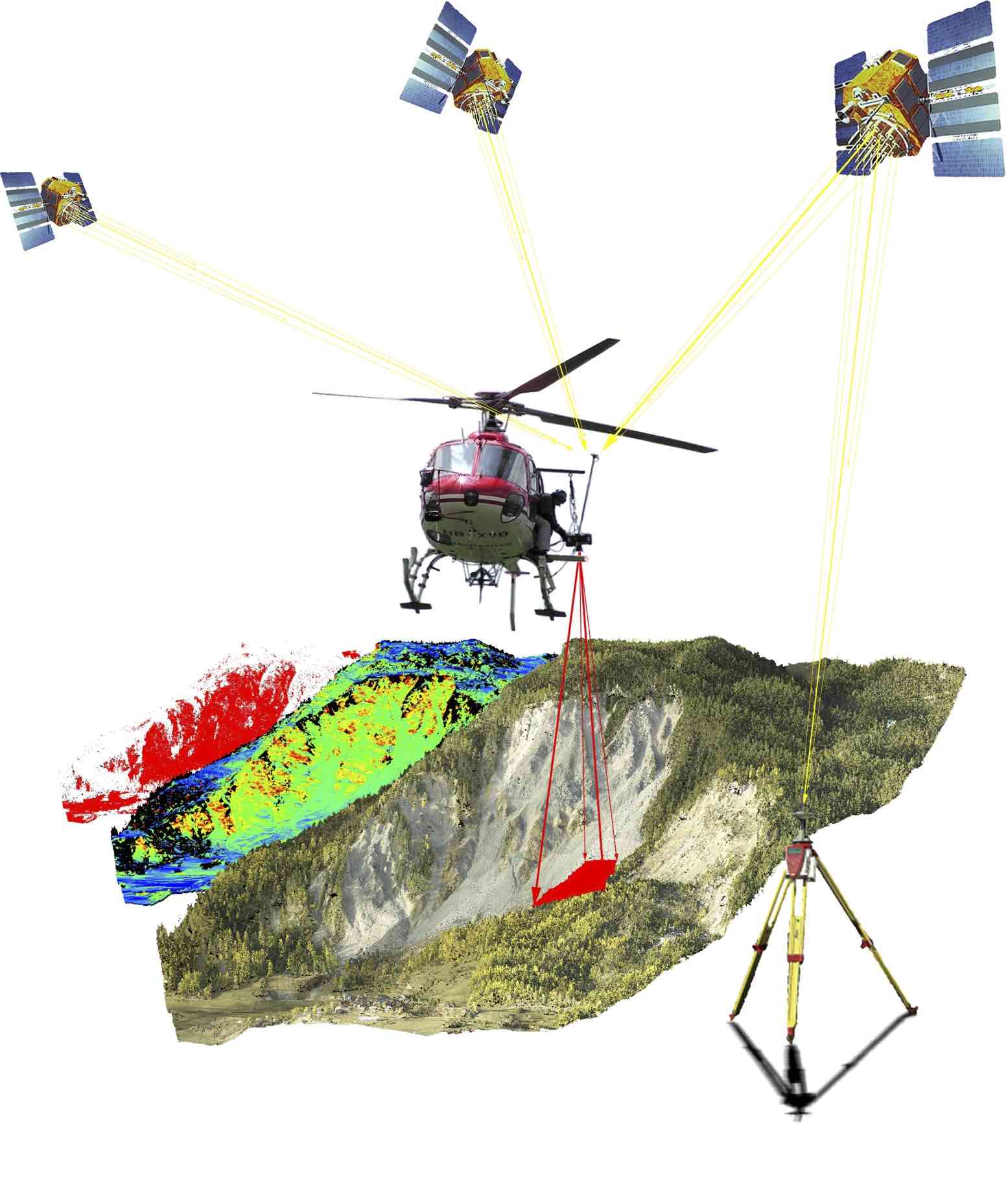 | Content
Support for 1 & 2: Polycopie No. 335 Optical Sensing in Mapping (Ch. 3, 5) printed: price of ~100 pages, PDF: via Moodle (see link below) Assistant contact hours: during exercises |
- Announcements (Forum)
- Complementary reading: Springer Handbook GIS (2022), Chapter 9. Data Acqusition (File)
- Agenda and objectives (File)
- Class Forum (Forum)
Image formation
This week we see how a digital image is formed in a perspective camera and what are the basic geometrical relations between image, camera and object frames. We also exercise how to correct image observations for lens distortions.
Teacher: Jan Skaloud / Devis Tuia
Assistants: Aurélien Brun, Kyriaki Mouzakidou, Jesse La Haye
- Lecture - Introduction to the course (File)
- Lecture - Introduction to optical sensing (File)
- Lecture - Image formation (File)
- Lab 01 - Description (File)
- Lab 01 - Code & Data (Folder)
- Lab 01 - Solution (Folder)
Keypoint detection, description and matching
This week we will see how detect salient keypoints in images, describe them in terms of features, and how to use those to find correspondences that can be used for matching.
Teacher: D. Tuia
Assistants: E. Dalsasso, J. Sauder
Image orientation
This week we see how to orient and calibrate an image from known points and practice it with one method using the observations from Ex. 1. We also get acquainted with the basics of depth determination in a stereo-vision system.
Teacher: Jan Skaloud
Assistants: Jesse La Haye, Antoine Carreau
- Lecture - Image orientation (File)
- Lab 03 - Description (File)
- Lab 03 - Code & Data (Folder)
- Lab 03 - Solution (File)
Stereo vision
We will first see how to obtain depth from a stereo-pair of oriented images, then how to infer the relative orientation (pose) of two cameras from point-to-point correspondences (key-point matches). This process can generalise to multiple-views (images).
Teacher: Jan Skaloud
Assistants: Jesse LaHaye, Antoine Carreau
- Lecture - Stereo vision (File)
- Lab 04 - Description (File)
- Lab 04 - Code & Data (Folder)
- Lab_4 Grades (File)
Mapping products: DEM and ortho-photo
In this week we will see how obtain a dense 3D point-cloud from the globally optimised (oriented and calibrated) images and how to transform it to a digital elevation model (DEM). The DEM, together with the oriented photos is then used for creating an ortho-photo (=ortho-image), that similarly to a plan/map has correct distances over the whole scene.
Teacher: Jan Skaloud
Assistants: Jesse LaHaye, Antoine Carreau
- Lecture - Optimisation & Mapping (File)
- Exercise on mission planning & appendix on other mapping aspects (File)
- Lab 5 - Description (File)
- Lab 05 - Agisoft quick guide (File)
Feature extraction from the DEM
This week we will see how extract spatial features from a digital elevation model (like directional derivatives, slopes, etc) and from images.
These features will be then re-used in the following weeks to train machine learning algorithms.
Teacher: D. Tuia
Assistants: H. Porta, G. Sümbül
Important: There will be no exercise on Friday. The "features" exercise will be next Friday.
In this short lecture we will discuss what is machine learning and go through the main families of methods with some examples.
On Friday, we will have the exercise on feature extraction (relative to the course you had on the 27.03)
Teacher: D. Tuia
Assistants: H. Porta, E. Dalsasso
Friday 11 April: exercise on regression
This week we will see how to use the spatial features extracted from the digital elevation model (like directional derivatives, slopes, etc) into a machine-learning pipeline for regression. We will revise linear regression (uni and multivariate) and then see the random forests model.
Team: D. Tuia, G. Sumbul, E. Dalsasso, H. Porta
Part dedicated to Geostatistics
Teacher: Alexis Berne
Assistants: G. Ghiggi and M. Guidicelli
- Chap.1 (File)
- Basic stat reminder (File)
- Video - session 20250417 Geostat 1 (URL)
- Ex. Geostat. 1 (File)
- R code (File)
- R tutorial (File)
- Ex.1 - solutions (File)
- Chap.2 (File)
- Ex. Geostat. 2 (File)
- R code (File)
- Ex.2 - solutions (File)
- Video - session 20250501 (URL)
- Session 2 - pictures (thanks to S. Hominal) (File)
- Ex. Geostat. 3 (File)
- R code (File)
- Ex.3 - solutions (File)
- Video - session 20250508 (URL)
- Session 3 - pictures (thanks to S. Hominal) (File)
- Chap.3 (File)
- Ex. Geostat. 4 (File)
- Data ex.4 (File)
- R code (File)
- Ex.4 - solutions (File)
- Video - session 20250515 (URL)
- Session 4 - pictures (thanks to S. Hominal) (File)
- Video - session 5 (URL)
- Session 5 - picture (thanks to S. Hominal) (File)
- Ex. Geostat. 5 (File)
- R code (File)
- Data ex.5 (File)
- Ex.5 - solutions (File)